The Future of Green Transportation in US are Hydrogen Powered Cars. In recent years, the automotive industry has witnessed significant advancements in sustainable transportation options. One promising technology that has gained attention is hydrogen-powered cars. These vehicles utilize hydrogen as a fuel source, offering a clean and efficient alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
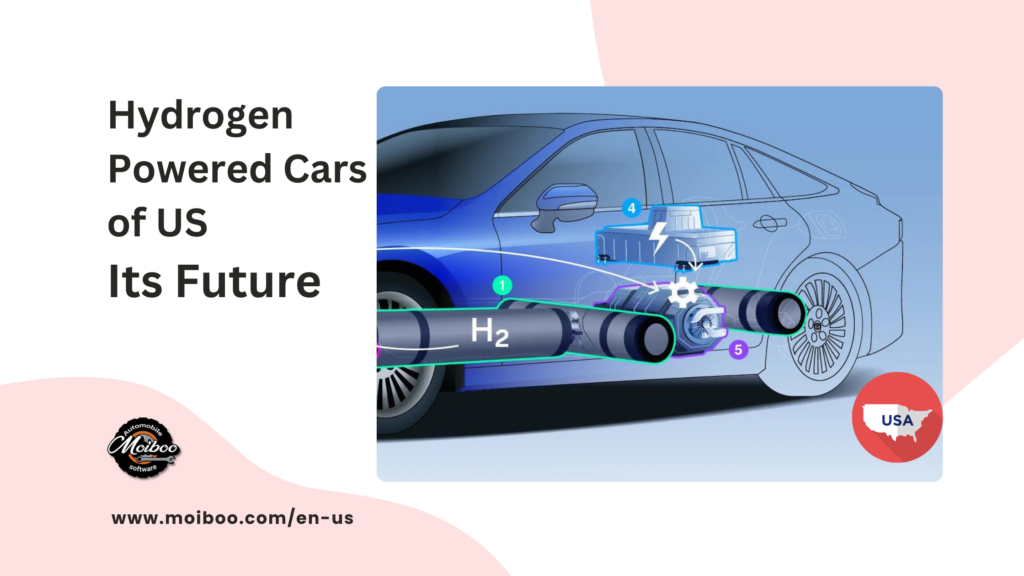
In this blog, we will delve into the world of hydrogen powered cars, focusing on the hydrogen internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle.
Discover the benefits, challenges, and the current state of hydrogen powered cars in the US.
Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles:
- Operate similarly to gasoline cars but use hydrogen as fuel instead.
- Hydrogen is injected into the engine’s combustion chamber, mixing with air and igniting to generate mechanical power.
Advantages of Hydrogen ICE Vehicles:
- Easy integration into existing infrastructure, can be refueled at conventional gasoline stations.
- Zero-emission vehicles, as the only byproduct of hydrogen combustion is water vapor.
- Comparable power and acceleration to conventional gasoline cars.
- Refueling time is similar to gasoline-powered vehicles, eliminating range anxiety.
Challenges:
- Limited availability of hydrogen refueling infrastructure, particularly in certain regions of the US.
- Logistical challenges in hydrogen production and transportation.
Hydrogen powered cars are designed with safety in mind and undergo rigorous testing to ensure their safe operation. Here are some key points regarding the safety of hydrogen powered cars:
- Fuel System Safety: Hydrogen fuel systems in vehicles are designed to be safe and secure. They incorporate multiple safety features, such as sensors, valves, and pressure relief devices, to prevent leaks and maintain system integrity.
- Hydrogen Storage: Hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks or as a cryogenic liquid in hydrogen-powered cars. These storage methods are carefully engineered to withstand extreme conditions and prevent leaks. Tank materials are selected for their strength and resistance to hydrogen embrittlement.
- Crashworthiness: Hydrogen-powered cars are subject to the same rigorous safety standards and crash tests as conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. Automakers design these vehicles to protect occupants in the event of a collision, ensuring structural integrity and appropriate placement of hydrogen storage systems.
- Leak Detection and Mitigation: Hydrogen fuel systems are equipped with sophisticated leak detection systems that monitor for any potential leaks. In the event of a detected leak, safety measures, such as automatic shut-off valves, are in place to mitigate any risks.
- Fire Safety: While hydrogen is a flammable gas, hydrogen-powered cars are engineered with multiple safety measures to minimize the risk of fire. These include the use of materials that resist combustion, flame arrestors, and rapid dispersal systems in case of a leak.
- Safety Regulations and Standards: Regulatory bodies, such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States, establish safety regulations and standards for hydrogen-powered vehicles. Automakers adhere to these regulations and undergo extensive testing and certification processes to ensure compliance.
- Industry Collaboration and Research: Automakers, research institutions, and organizations collaborate to continuously improve the safety of hydrogen-powered cars. They conduct extensive research and development to address any safety concerns and implement advancements in technology.
Both hydrogen powered cars and electric cars have their own advantages and considerations. Here’s a comparison of the two:
Hydro-powered Cars:
- Advantages:
- Use renewable energy: Hydrogen powered cars generate energy from water, which is a renewable resource.
- Lower emissions: Hydrogen powered cars produce minimal or zero emissions during operation.
- Potential for long-range driving: Hydrogen fuel cells can provide longer driving ranges compared to electric batteries.
- Considerations:
- Limited infrastructure: Hydrogen refueling stations are currently less common and widespread compared to electric charging stations.
- Production challenges: The production of hydrogen fuel and establishing the necessary infrastructure can be complex and costly.
- Energy efficiency: Hydrogen production can be energy-intensive, and there are some energy losses in the conversion process.
Electric Cars:
- Advantages:
- Zero emissions: Electric cars produce no tailpipe emissions, helping to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Expanding charging infrastructure: Electric charging stations are becoming increasingly available, making charging more convenient.
- Energy efficiency: Electric cars have high energy efficiency, especially when considering the use of renewable energy sources for charging.
- Considerations:
- Limited driving range: Electric cars generally have a shorter driving range compared to some hydro-powered vehicles.
- Charging time: Charging an electric car takes longer compared to refueling a hydrogen-powered vehicle.
- Battery production and disposal: Electric car batteries require resources for production and proper disposal or recycling.
Promoting Adoption in the US:
- Government and private industry investing in research, infrastructure expansion, and financial incentives.
- Automakers introducing hydrogen ICE vehicles to the market.
Future Outlook:
- Hydrogen powered cars have the potential to play a significant role in the future of the automotive industry.
- Advancements in technology, infrastructure support, and growing environmental awareness drive their potential.
- Overcoming challenges will be crucial for widespread adoption.
Conclusion:
- Hydrogen powered cars, including hydrogen ICE vehicles, offer a promising solution for sustainable transportation.
- Zero-emission nature, compatibility with existing infrastructure, and comparable performance make them attractive.
- Ongoing advancements and investments in hydrogen technology indicate a positive trajectory.
- Embracing hydrogen as a fuel source can drive us towards a cleaner and greener future.
